Culinary influences
Discover 10 "foreign" foods that are actually American

Image: Dyana Wing So
In the United States—the great melting pot—we have embraced countless delicious dishes brought by immigrants when they arrived in America. At the same time, this cultural exchange gave rise to new recipes that, while borrowing elements from cuisines around the world, were created entirely on American soil. For example, did you know that no one in Italy would serve meatballs and pasta in the same course? Or that there isn’t a single restaurant in Cuba where you can order an authentic Cuban sandwich? Read on to discover 10 dishes you thought were foreign but are, in fact, American!
1
Chimichangas

Image: Pedro Gil
What do you mean it’s not a Mexican dish? The name sounds Mexican!" While two Mexican-American restaurants—one in Tucson and the other in Phoenix—dispute the authorship of this dish, one thing is certain: it originated in the United States, more specifically in Arizona .
Today, chimichangas— a stuffed burrito fried in oil or butter —are one of America’s favorite dishes. And although they could never have existed without the culinary influence of our southern neighbor, we also had a lot to do with their creation.
2
Chop suey

Image: Albert Stoynov
There are many theories about the origin of this popular dish, but one of the most widespread is particularly intriguing. According to lore, chop suey was invented in 1896 by the cook of the Chinese ambassador to the United States . Apparently, the diplomat, who was hosting a dinner for American guests, instructed the chef to prepare a dish that would appeal to both Eastern and Western palates.
While there is no dispute that similar dishes exist in Asian cuisine, this particular moment of cultural and culinary exchange is said to have sparked the American public's fascination with Asian flavors . Soon after, Chinese restaurants began to proliferate across the country, with chop suey as their signature dish.
3
Russian dressing

Image: Rachel Claire
Did you know that nobody in Russia has ever seasoned their salad with Russian dressing? It doesn't exist there! This popular condiment is a completely American invention. It’s believed to have been created by a New Hampshire butcher in the early 20th century , who originally called it "Russian mayonnaise." Interestingly, he had no known ties to Russia, so it is unclear why he chose that name.
Perhaps the answer lies in one of the dressing’s original ingredients: black caviar, one of Russia’s most famous exports . Unfortunately, we’ll probably never know the full story. One thing is certain, though—Russian dressing was born in the United States!
4
Chili con carne

Image: https://images.unsplash.com/photo-1545433243-0a87e3fed9b4?q=80&w=1470&auto=format&fit=crop&ixlib=rb-4.0.3&ixid=M3wxMjA3fDB8MHxwaG90by1wYWdlfHx8fGVufDB8fHx8fA%3D%3D
Okay, chili may sound like a traditional Mexican dish, but this meaty version, chili con carne , was actually created in South Texas in the late 19th century . Not only did it feature added animal protein, but one of the key ingredients often associated with chili today—beans—was originally left out.
Chili con carne quickly became a national favorite. Families across the country began experimenting with their own versions, and soon, nearly every state had its own take on the dish . But nothing quite compares to the original Texan chili—the one that started it all!
5
Fortune cookies

Image: hannahlouise123
If you asked someone where fortune cookies come from, they’d probably say China. After all, they’re the quintessential treat served at Chinese restaurants around the world. But surprisingly, fortune cookies were invented in the United States —and they’re not even Chinese !
They were first created in the early 20th century in San Francisco , one of the American cities with the largest Asian immigrant populations. Even more surprisingly, they were invented by a Japanese man as a gesture of gratitude to the mayor who had hired him as a designer. He was inspired by a Kyoto tradition called omikuji , which involves offering a treat that contains a random fortune written on a slip of paper.
After World War II, many Chinese entrepreneurs took over Japanese bakeries in the Bay Area, helping to spread the cookie's popularity—and contributing to the common misconception about their origin.
6
Cuban sandwich

Image: Conor Brown
Despite its name, the Cuban sandwich originated in the Cuban-American communities of Ybor City, Key West , and Plant City , Florida , in the early 20th century. It later became popular in Miami and other American cities with large Cuban populations.
Interestingly, the ingredients vary from place to place. What all versions share, however, is Cuban bread —similar to a French baguette but made with slightly different ingredients and a unique baking method. So, is this bread authentically Cuban? Not exactly. It was actually created alongside the sandwich, right here in the United States!
7
German chocolate cake
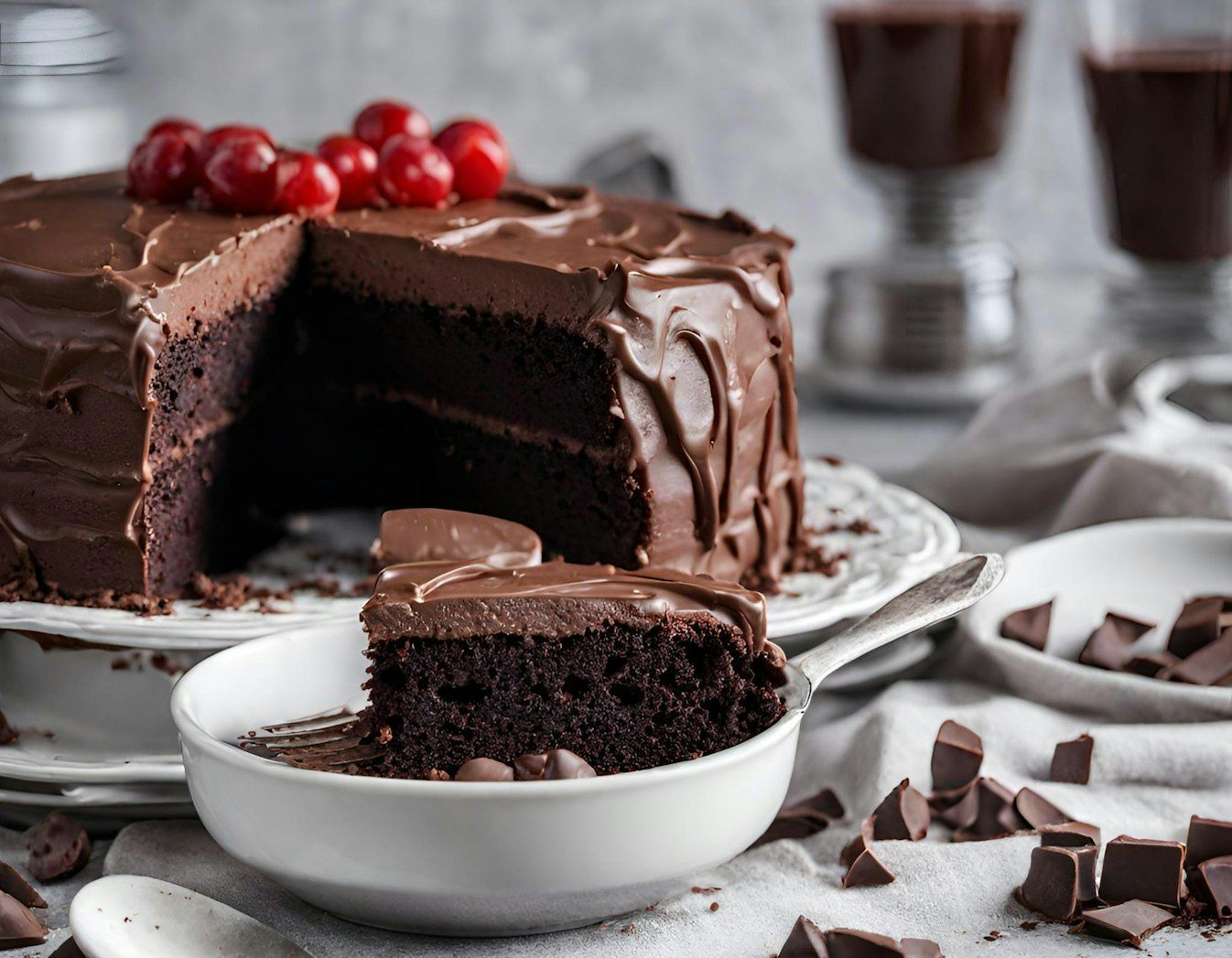

Image: BraggsDiner
Despite its name, German chocolate cake has no culinary ties to Germany, nor is it named in honor of the country. In fact, it takes its name from Samuel German , a confectioner who, in the mid-1850s, developed a type of baking chocolate for the Baker's Chocolate Company of Boston, Massachusetts.
A century later, a recipe using German’s Sweet Chocolate appeared in the Dallas Morning News and became an instant hit among homemakers. Before long, Baker's Chocolate sales soared, marking a strong comeback for German's baking bar. Today, German chocolate cake is an American classic —and now you know its true origin!
8
Spaghetti and meatballs
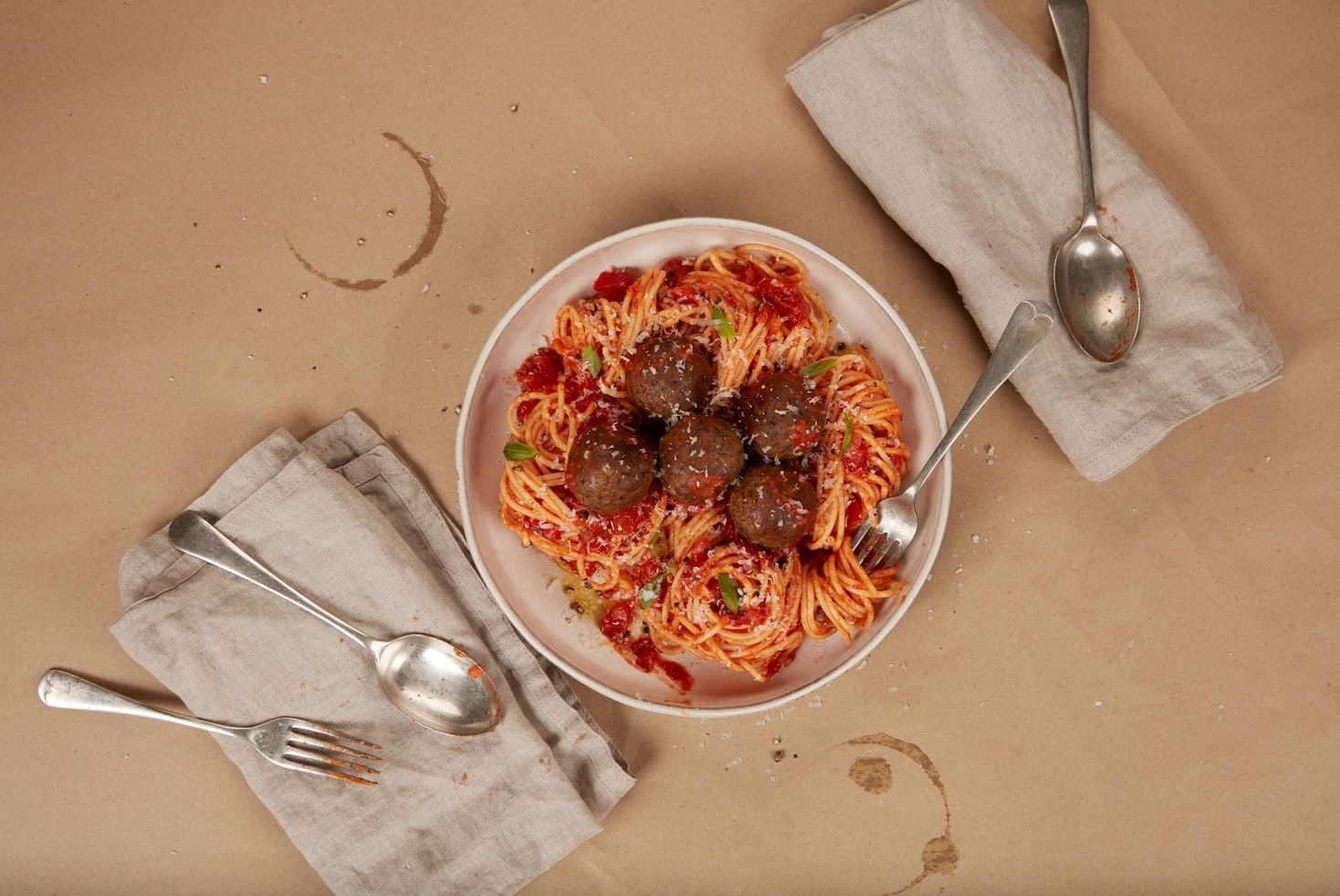

Image: Ivy Farm
You probably thought this dish was authentically Italian your whole life. Well, we hate to break it to you, but spaghetti and meatballs are a hundred percent American invention, though it is, to be fair, a product of early 20th-century Italian immigration.
Meatballs were likely inspired by Italian polpette , a stew made of small balls of breadcrumbs mixed with meat or fish. However, in the Old World, polpette was never served with pasta and marinara sauce; it was a dish on its own. When Italian immigrants discovered how easy it was to buy beef in America, they began incorporating it into many dishes. And thank goodness they did!
9
Garlic bread
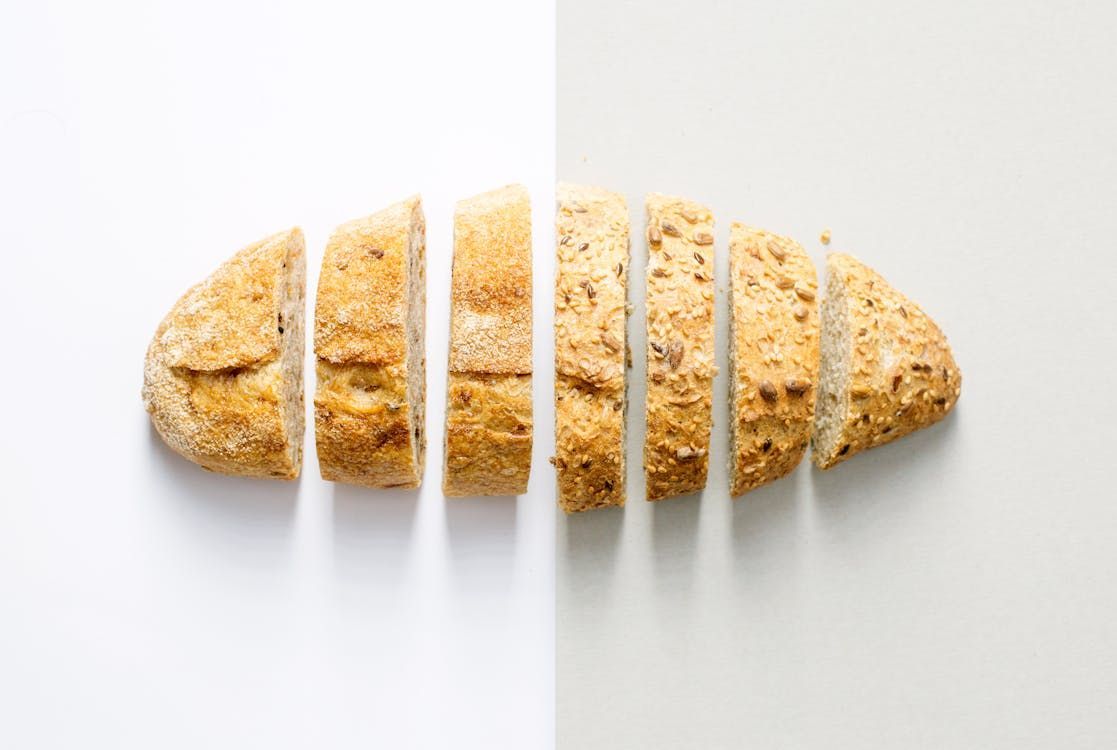

Image: Mariana Kurnyk
Another food with Italian influences but created in the United States is garlic bread. A staple of Italian restaurants, this side dish was introduced by immigrants who were likely trying to emulate the famous bruschetta .
However, they ran into an obstacle that led to the invention of something totally new—but just as delicious. Olive oil, so abundant in the mother country, was scarce and difficult to obtain in America. Therefore, they resorted to an ingredient found in abundance here: butter . And the rest is history!
10
Vichyssoise
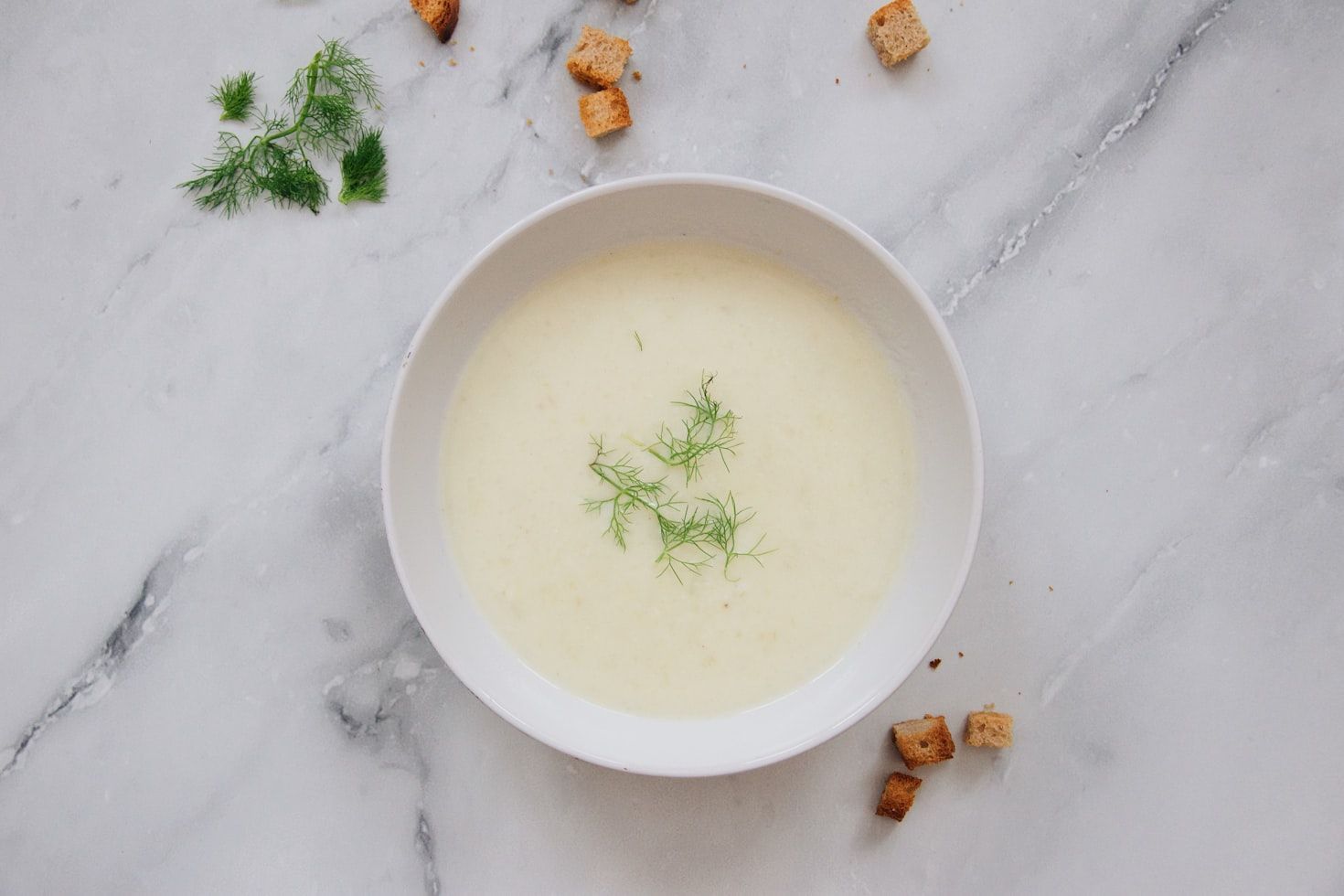

Image: Julia Kicova
With such a name, you might think this dish is purely French! Well, not exactly. Although it was created by a French-born chef, it was first made in Manhattan, New York. In 1917, feeling a bit homesick for his homeland, Louis Diat, head chef of the Ritz-Carlton Hotel, wanted to recreate a potato and leek soup his mother used to make when he was growing up in Montmarault, France.
But there was a problem: it was summer. Finally, he came up with a brilliant idea—to thin down the hot soup with cold milk and cream . He named his invention after Vichy, the famous spa town near his hometown. The dish was an instant hit among the restaurant’s guests, who soon asked for it to be available year-round.